Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 in NaCl
in NaClAoyama, Takahito; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Kato, Chiaki; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Metals, 11(3), p.511_1 - 511_13, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.75(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The effect of Cu in bulk solution on pitting corrosion resistance of extra high purity type 316 stainless steel was investigated. Pitting occurred in 0.1 M NaCl-1 mM CuCl
in bulk solution on pitting corrosion resistance of extra high purity type 316 stainless steel was investigated. Pitting occurred in 0.1 M NaCl-1 mM CuCl whereas pitting was not initiated in 0.1 M NaCl. Although deposition of Cu
whereas pitting was not initiated in 0.1 M NaCl. Although deposition of Cu on the surface occurred regardless of potential region in 0.1 M NaCl-1 mM CuCl
on the surface occurred regardless of potential region in 0.1 M NaCl-1 mM CuCl , Cu
, Cu in bulk solution had no influence on the passive film formation. The decrease in pitting corrosion resistance in 0.1 M NaCl-1 mM CuCl
in bulk solution had no influence on the passive film formation. The decrease in pitting corrosion resistance in 0.1 M NaCl-1 mM CuCl resulted from the deposited Cu or Cu compound and continuous supply of Cu
resulted from the deposited Cu or Cu compound and continuous supply of Cu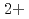 on the surface.
on the surface.
Fuji, Hiroyuki*; Aoki, So; Ishii, Tomohiro*; Sakai, Junichi*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 64(5), p.178 - 182, 2015/05
This study focused on a breakdown of passive film which is followed by rust staining, and the objective of this study was to clarify the effect of stability of passive film on the resistance of rust staining of stainless steels. Atomospheric exposure test was carried out for 12 months. In order to compare the stability of passive film, measurements of potential-decay curves, and potentiostatic polarization tests were performed in acidic aqueous chloride solution. As a result, rust area of austenitic stainless steel was higher than that of ferritic stainless steel. This order didn't follow the orders of pitting potentials and densities of inclusions on surface between specimens. On the contrary, the order of the resistance of rust staining of stainless steels followed the order of the stability of passive film. One of the reasons why the resistance of rust staining of austenitic stainless steel was worse than that of ferritic stainless steel was seemed that chloride more easily broke passive film on the surface of austenitic stainless and formed micro pits which become initiations of rust staining and increase density of stains.
; *
JAERI-M 83-137, 26 Pages, 1983/09
no abstracts in English
; ; Kondo, Tatsuo
JAERI-M 8786, 19 Pages, 1980/03
no abstracts in English